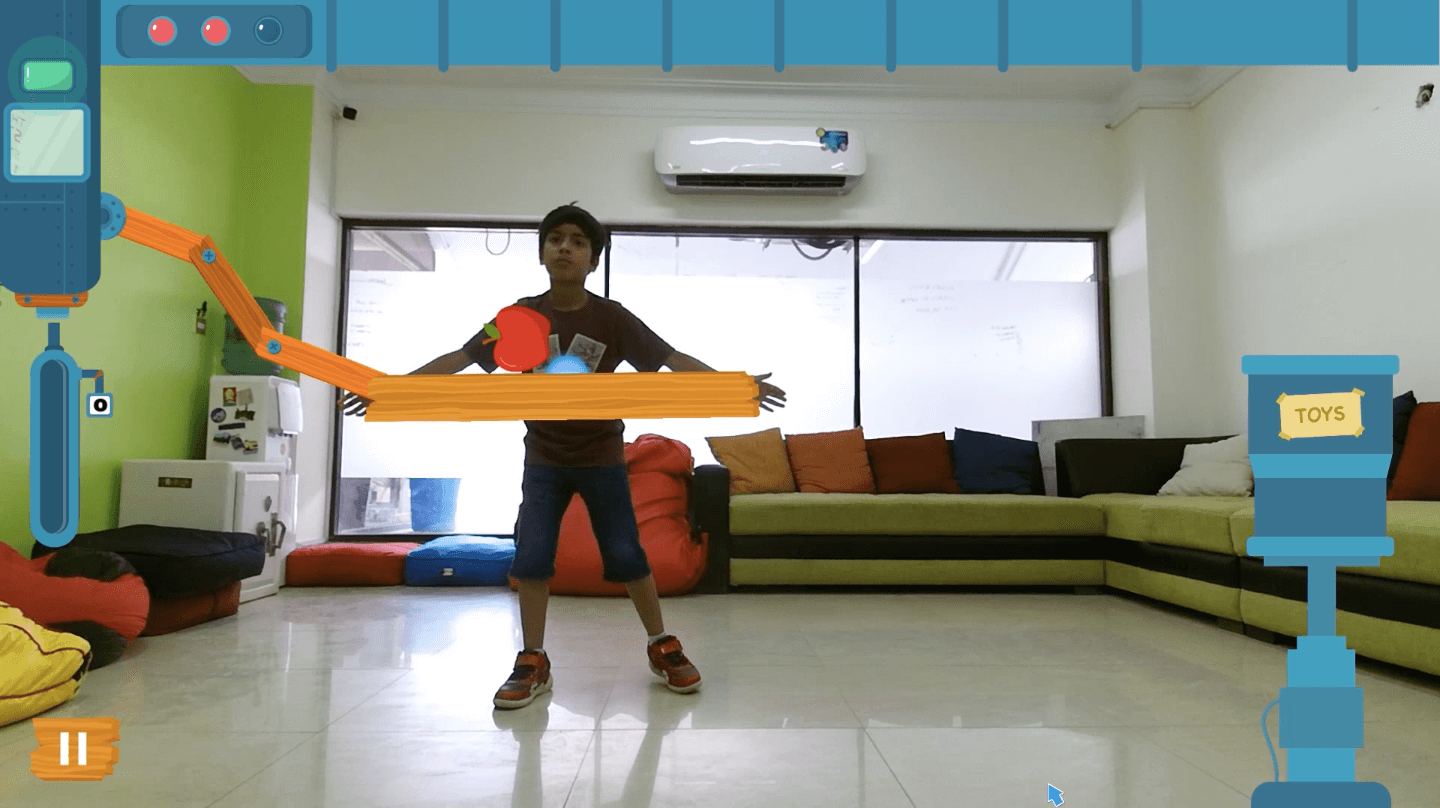
Have you ever become speechless at your child’s unique questions?
For example, why is the sky blue, what’s this, how it works, why this and that, and a hundred more exploratory questions in a day, that might leave you with no answer. But that’s not chatter, it’s their endless curiosity about their surroundings. All thanks to cognitive development in early childhood!
Cognitive development in early childhood is the most crucial phase for developing a child’s learning, exploring, understanding, and problem-solving skills. But do you know what cognitive development is, and why it is important for childhood development?
Understanding cognitive development is key to providing your children with the best, making everyday moments more meaningful. Let’s explore what cognitive development in early childhood is, its different stages, and activities to sharpen cognitive skills in young children.
What is Cognitive Development in Early Childhood?
Cognitive development in early childhood is how young children start thinking, exploring, and understanding their surroundings from an early age. It includes solving problems, remembering things, paying attention, and understanding cause and effect. When children ask questions out of curiosity, recognize and identify patterns, and make sense of the world, it supports their reading, math, and logical thinking. The cognitive development definition in early childhood refers to the mental growth over time that shapes how children process everything around them.
Importance of Cognitive Development in Early Childhood:
Strong cognition in early childhood contributes significantly to a child’s future learning and success. When children develop cognitive skills at a young age, they become efficient problem-solvers, curious learners, and strong decision-makers. Simple everyday activities like reading stories, puzzles, or asking them questions can boost their brain function. Cognitive growth during these early years (from birth to age 8) readies them for lifelong learning and school, both in and out!
Stages of Cognitive Development in Early Childhood:
Cognitive development in early childhood consists of different stages that alter how children think, explore, and make sense of their surroundings. These stages are part of a child’s growth and learning journey from birth to early childhood. These stages were originally proposed by psychologist Jean Piaget, who studied the evolving nature and development of children’s thinking as they grow. Key childhood cognitive development stages include:
- Sensorimotor Stage (Birth-2 years): It involves learning through senses and movement, like grasping and looking.
- Preoperational Stage ( 2-7 years): Children develop imagination, memory, and language, and think in a very concrete way, which lacks logic.
- Concrete Operational Stage ( 7-11 years): Children start thinking more logically about real-life situations and understand rules properly.
- Formal Operational Stage ( 12+ years): Thinking and reasoning become more abstract, logical, and organized, like young adults.
Piaget’s theory of cognitive development helps parents and educators understand the pattern of a child’s mind through different stages, so they can provide the right support at each phase of childhood development.
Aspects of Cognitive Development in Early Childhood:
Childhood cognitive aspect refers to all the mental skills children build as they grow. These aspects are pillars to develop love for lifelong learning, clear communication, and effective decision-making. Major aspects of cognitive development include:
- Memory: Learning and recalling information.
- Attention: Focusing on tasks without getting easily distracted.
- Language Development: Learning to understand and use new words.
- Problem-Solving: Analyzing and trying different ways to solve problems and reach goals.
- Thinking Skills: Understanding basic concepts like size, numbers, and time..
Cognitive Development in Early Childhood (ages 2 to 6):
Cognitive development in preschoolers ( from 2 to 6 years) marks the phase when children start thinking better and smarter. Children bring up new ideas, understand symbols, ask questions constantly, and pretend play during this stage. Young brains at this age absorb information more quickly than at any other stage.
This period is important for laying the groundwork for language, memory, and critical thinking skills. Encouraging cognitive development in preschoolers with interactive activities, storytelling, and real-life conversations helps them build skills effectively and succeed in life.
Examples of Cognitive Development in Early Childhood:
Cognitive development during early childhood can be seen in everyday moments as children start thinking, exploring, and making sense of their surroundings. Each action and activity becomes more meaningful at this stage. Common, everyday examples include:
- Sorting toys or blocks by colors, shapes, or sizes
- Understanding and following simple instructions
- Solving puzzles and matching games
- Asking interrogative questions
- Pretend play that reflects imagination and memory
Activities for Cognitive Development in Early Childhood:
Here are some activities that can help in cognitive development in early childhood and strengthen cognitive skills in children:
- Reading books with pictures or flashcards
- Solving puzzles or playing matching games
- Building blocks
- Singing songs with actions and rhymes
- Doing age-appropriate science experiments
How Wondergames Help in Cognitive Development:
Looking for ways to sharpen your child’s cognitive skills and learning, while keeping them entertained? Don’t worry, we’ve got you covered! WonderGames are not just fun but a smart and engaging way to support cognitive development in children of all ages, especially for children with special needs.
WonderTree’s interactive games like BRAIN GRUB and SCOOP’D are perfect for developing cognitive skills in children at their own pace. These games help improve important skills like decision-making, object recognition, and hand-eye coordination—all through fun and play. Turn your child’s screen time into growth time with WonderTree!
Explore more Wondergames, and sign up for a 14-day free trial today!
Frequently Asked Questions:
What is cognitive development in early childhood?
Cognitive development in early childhood is how children begin to think, learn, explore, and solve problems. It helps them understand their surroundings and prepare them for long-term learning in school and life.
What are the 4 stages of cognitive development?
According to Piaget, there are 4 stages of cognitive development, showing change and evolution in thinking and understanding of children over time. The 4 stages of cognitive development include:
- Sensorimotor (0-2 years)
- Preoperational (2-7 years)
- Concrete Operational (7-11 years)
- Formal Operational (12+ years)
What is an example of cognitive development?
A basic, everyday example of cognitive development is when children learn to sort blocks by color or shape. It showcases their learning and understanding abilities by recognizing patterns and solving small problems.
What is the cognitive approach in early childhood?
The cognitive approach in early childhood is how kids think, process information, and learn new things from their surroundings. It encourages everyday activities that enhance memory, problem-solving, and decision-making skills.
What are the stages of cognitive development in childhood?
Cognitive development in early childhood goes through different stages, like identifying objects, using speech, understanding cause and effect, and building planning or problem-solving skills. Each stage allows children to grow smarter, independent, and more confident.
What are cognitive strategies for kids?
Cognitive strategies for kids include basic tools like pictures or flashcards to make them remember things, repeating instructions, breaking tasks into simple steps, and asking questions for enhanced clarity. These strategies help improve thinking, focus, and learning in children.